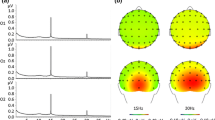
Summary
In everyday life specific situations need specific reactions. Through repetitive practice, such stimulus-response associations can be learned and performed automatically. The aim of the present EEG study was the illustration of learning dependent modifications in neuronal pathways during short-term practice of visuomotor associations. Participants performed a visuomotor association task including four visual stimuli, which should be associated with four keys, learned by trial and error. We assumed that distinct cognitive processes might be dominant during early learning e.g., visual perception and decision making. Advanced learning, however, might be indicated by increased neuronal activation in integration- and memory-related regions. For assessment of learning progress, visual- and movement-related brain potentials were measured and compared between three learning stages (early, intermediate, and late). The results have revealed significant differences between the learning stages during distinct time intervals. Related to visual stimulus presentation, Low Resolution Electromagnetic Brain Tomography (LORETA) revealed strong neuronal activation in a parieto-prefrontal network in time intervals between 100–400 ms post event and during early learning. In relation to the motor response neuronal activation was significantly increased during intermediate compared to early learning. Prior to the motor response (120–360 ms pre event), neuronal activation was detected in the cingulate motor area and the right dorsal premotor cortex. Subsequent to the motor response (68–430 ms post event) there was an increase in neuronal activation in visuomotor- and memory-related areas including parietal cortex, SMA, premotor, dorsolateral prefrontal, and parahippocampal cortex. The present study has shown specific time elements of a visuomotor-memory-related network, which might support learning progress during visuomotor association learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amunts, K., Schleicher, A., Ditterich, A. and Zilles, K. Broca’s region: Cytoarchitectonic asymmetry and developmental changes. J. Comp Neurol. 2003, 465: 72–89.
Annett, M. Five tests of hand skill. Cortex, 1992, 28: 583–600.
Bender, S., Oelkers-Ax, R., Resch, F. and Weisbrod, M. Motor processing after movement execution as revealed by evoked and induced activity. Brain Res. Cogn Brain Res. 2004, 21: 49–58.
Brasted, P.J. and Wise, S.P. Comparison of learning-related neuronal activity in the dorsal premotor cortex and striatum. Eur J Neurosci. 2004, 19(3), 721–740.
Bush, G., Luu, P. and Posner, M.I. Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends Cogn Sci. 2000, 4: 215–222.
Cohen, J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York: Academic Press. 1977.
Deiber, M.P., Ibanez, V., Honda, M., Sadato, N., Raman, R. and Hallett, M. Cerebral processes related to visuomotor imagery and generation of simple finger movements studied with positron emission tomography. NeuroImage. 1998, 7: 73–85.
Elliott, R., Dolan, R.J. and Frith, C.D. Dissociable functions in the medial and lateral orbitofrontal cortex: Evidence from human neuroimaging studies. Cereb. Cortex. 2000, 10: 308–317.
Epstein, R. and Kanwisher, N. A cortical representation of the local visual environment. Nature. 1998, 392: 598–601.
Esslen, M., Pascual-Marqui, R.D., Hell, D., Kochi, K. and Lehmann, D. Brain areas and time course of emotional processing. NeuroImage. 2004, 21: 1189–1203.
Faillenot, I., Toni, I., Decety, J., Gregoire, M.C. and Jeannerod, M. Visual pathways for object-oriented action and object recognition: Functional anatomy with PET. Cereb. Cortex. 1997, 7: 77–85.
Garavan, H., Ross, T.J. and Stein, E.A. Right hemispheric dominance of inhibitory control: An event-related functional MRI study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1999, 96: 8301–8306.
Goodale, M.A. and Milner, A.D. Separate visual pathways for perception and action. Trends Neurosci. 1992, 15: 20–25.
Grafton, S.T. Cortical control of movement. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 36: 3–4.
Gray, C.M., Konig, P., Engel, A.K. and Singer, W. Oscillatory responses in cat visual cortex exhibit inter-columnar synchronization which reflects global stimulus properties. Nature. 1989, 338: 334–337.
Halsband, U. and Passingham, R.E. Premotor cortex and the conditions for movement in monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Behav. Brain Res. 1985, 18: 269–277.
Hammond, G.R. and Fox, A.M. Electrophysiological evidence for lateralization of preparatory motor processes. Neuroreport. 2005, 16: 559–562.
Hester, R.L., Murphy, K., Foxe, J.J., Foxe, D.M., Javitt, D.C. and Garavan, H. Predicting success: Patterns of cortical activation and deactivation prior to response inhibition. J. Cogn Neurosci. 2004, 16: 776–785.
Heyder, K., Suchan, B. and Daum, I. Cortico-subcortical contributions to executive control. Acta Psychol. (Amst). 2004, 115: 271–289.
Holm, S. A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Statistics. 1979, 6, 65–70.
Honda, M., Deiber, M.P., Ibanez, V., Pascual-Leone, A., Zhuang, P. and Hallett, M. Dynamic cortical involvement in implicit and explicit motor sequence learning. A PET study. Brain. 1998, 121 (Pt 11): 2159–2173.
Inoue, K., Yamashita, T., Harada, T. and Nakamura, S. Role of human SII cortices in sensorimotor integration. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113: 1573–1578.
Jackson, P.L., Lafleur, M.F., Malouin, F., Richards, C.L. and Doyon, J. Functional cerebral reorganization following motor sequence learning through mental practice with motor imagery. NeuroImage. 2003, 20: 1171–1180.
Jackson, S.R., Jackson, G.M. and Roberts, M. The selection and suppression of action: ERP correlates of executive control in humans. Neuroreport. 1999, 10: 861–865.
Jancke, L., Kleinschmidt, A., Mirzazade, S., Shah, N.J. and Freund, H.J. The role of the inferior parietal cortex in linking the tactile perception and manual construction of object shapes. Cereb. Cortex. 2001, 11: 114–121.
Jancke, L., Specht, K., Shah, J.N. and Hugdahl, K. Focused attention in a simple dichotic listening task: An fMRI experiment. Brain Res. Cogn Brain Res. 2003, 16: 257–266.
Johnson, P.B., Ferraina, S., Bianchi, L. and Caminiti, R. Cortical networks for visual reaching: Physiological and anatomical organization of frontal and parietal lobe arm regions. Cereb. Cortex. 1996, 6: 102–119.
Jordan, K., Heinze, H.J., Lutz, K., Kanowski, M. and Jancke, L. Cortical activations during the mental rotation of different visual objects. NeuroImage. 2001, 13: 143–152.
Jordan, K., Schadow, J., Wuestenberg, T., Heinze, H.J. and Jancke, L. Different cortical activations for subjects using allocentric or egocentric strategies in a virtual navigation task. Neuroreport. 2004, 15: 135–140.
Karni, A., Meyer, G., Rey-Hipolito, C., Jezzard, P., Adams, M.M., Turner, R. et al. The acquisition of skilled motor performance: Fast and slow experience-driven changes in primary motor cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1998, 95: 861–868.
Kawashima, R., Roland, P.E. and O’Sullivan, B.T. Functional anatomy of reaching and visuomotor learning: A positron emission tomography study. Cereb. Cortex. 1995, 5: 111–122.
Kringelbach, M.L. and Rolls, E.T. The functional neuroanatomy of the human orbitofrontal cortex: Evidence from neuroimaging and neuropsychology. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 72: 341–372.
Kurata, K., Tsuji, T., Naraki, S., Seino, M. and Abe, Y. Activation of the dorsal premotor cortex and pre-supplementary motor area of humans during an auditory conditional motor task. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 84: 1667–1672.
Lehmann, D., Ozaki, H. and Pal, I. EEG alpha map series: Brain micro-states by space-oriented adaptive segmentation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1987, 67: 271–288.
Manly, B.F.J. (1997). Randomization, Bootstrap and Monte Carlo Methods in Biology. (second ed.) Chapman & Hall, London.
Matelli, M. and Luppino, G. Parietofrontal circuits: Parallel channels for sensory-motor integrations. Adv. Neurol. 2000, 84: 51–61.
Matsumoto, R., Ikeda, A., Ohara, S., Matsuhashi, M., Baba, K., Yamane, F. et al. Motor-related functional subdivisions of human lateral premotor cortex: Epicortical recording in conditional visuomotor task. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114: 1102–1115.
Michel, C.M., Thut, G., Morand, S., Khateb, A., Pegna, A.J., Grave, d.P. et al. Electric source imaging of human brain functions. Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 36: 108–118.
Mulert, C., Jager, L., Pogarell, O., Bussfeld, P., Schmitt, R., Juckel, G. et al. Simultaneous ERP and event-related fMRI: Focus on the time course of brain activity in target detection. Methods Find. Exp Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 24 Suppl D: 17–20.
Mulert, C., Jager, L., Schmitt, R., Bussfeld, P., Pogarell, O., Moller, H.J. et al. Integration of fMRI and simultaneous EEG: Towards a comprehensive understanding of localization and time-course of brain activity in target detection. NeuroImage. 2004a, 22: 83–94.
Mulert, C., Pogarell, O., Juckel, G., Rujescu, D., Giegling, I., Rupp, D. et al. The neural basis of the P300 potential. Focus on the time-course of the underlying cortical generators. Eur Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2004b, 254: 190–198.
Muller, R.A., Kleinhans, N., Pierce, K., Kemmotsu, N. and Courchesne, E. Functional MRI of motor sequence acquisition: Effects of learning stage and performance. Brain Res. Cogn Brain Res. 2002, 14: 277–293.
Nakamura, K., Sakai, K. and Hikosaka, O. Neuronal activity in medial frontal cortex during learning of sequential procedures. J Neurophysiol. 1998, 80: 2671–2687.
Nichols, T.E. and Holmes, A.P. Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: A primer with examples. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 15: 1–25.
Pascual-Marqui, R.D., Esslen, M., Kochi, K. and Lehmann, D. Functional imaging with low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (LORETA): A review. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 24 Suppl C: 91–95.
Passingham, R.E. Premotor cortex and preparation for movement. Exp. Brain Res. 1988, 70: 590–596.
Petit, L., Orssaud, C., Tzourio, N., Crivello, F., Berthoz, A., and Mazoyer, B. Functional anatomy of a prelearned sequence of horizontal saccades in humans. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16: 3714–3726.
Pfurtscheller, G., Zalaudek, K. and Neuper, C. Event-related beta synchronization after wrist, finger and thumb movement. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 109: 154–160.
Pizzagalli, D., Lehmann, D., Koenig, T., Regard, M. and Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Face-elicited ERPs and affective attitude: Brain electric microstate and tomography analyses. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 111: 521–531.
Rolls, E.T. The functions of the orbitofrontal cortex. Brain Cogn. 2004, 55: 11–29.
Rosenbaum, D.A. Human movement initiation: Specification of arm, direction, and extent. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1980, 109: 444–474.
Sakai, K., Hikosaka, O., Miyauchi, S., Sasaki, Y., Fujimaki, N. and Putz, B. Presupplementary motor area activation during sequence learning reflects visuo-motor association. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19: RC1.
Schubert, T., von Cramon, D.Y., Niendorf, T., Pollmann, S. and Bublak, P. Cortical areas and the control of self-determined finger movements: An fMRI study. Neuroreport. 1998, 9: 3171–3176.
Seitz, R.J., Canavan, A.G., Yaguez, L., Herzog, H., Tellmann, L., Knorr, U. et al. Representations of graphomotor trajectories in the human parietal cortex: Evidence for controlled processing and automatic performance. Eur J Neurosci. 1997, 9: 378–389.
Shima, K. and Tanji, J. Role for cingulate motor area cells in voluntary movement selection based on reward. Science. 1998, 282: 1335–1338.
Silva, L.R., Amitai, Y. and Connors, B.W. Intrinsic oscillations of neocortex generated by layer 5 pyramidal neurons. Science. 1991, 251: 432–435.
Sinai, A. and Pratt, H. High-resolution time course of hemispheric dominance revealed by low-resolution electromagnetic tomography. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114: 1181–1188.
Staines, W.R., Padilla, M. and Knight, R.T. Frontal-parietal event-related potential changes associated with practising a novel visuomotor task. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2002, 13: 195–202.
Stephan, K.M., Thaut, M.H., Wunderlich, G., Schicks, W., Tian, B., Tellmann, L. et al. Conscious and subconscious sensorimotor synchronization–prefrontal cortex and the influence of awareness. NeuroImage. 2002, 15: 345–352.
Strik, W.K., Fallgatter, A.J., Brandeis, D. and Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Three-dimensional tomography of event-related potentials during response inhibition: Evidence for phasic frontal lobe activation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 108: 406–413.
Thoenissen, D., Zilles, K. and Toni, I. Differential involvement of parietal and precentral regions in movement preparation and motor intention. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22: 9024–9034.
Toni, I., Ramnani, N., Josephs, O., Ashburner, J. and Passingham, R.E. Learning arbitrary visuomotor associations: Temporal dynamic of brain activity. NeuroImage 2001, 14: 1048–1057.
Toni, I., Rowe, J., Stephan, K.E. and Passingham, R.E. Changes of cortico-striatal effective connectivity during visuomotor learning. Cereb. Cortex. 2002a, 12: 1040– 1047.
Toni, I., Schluter, N.D., Josephs, O., Friston, K. and Passingham, R.E. Signal-, set- and movement-related activity in the human brain: An event-related fMRI study. Cereb. Cortex. 1999, 9: 35–49.
Toni, I., Shah, N.J., Fink, G.R., Thoenissen, D., Passingham, R.E. and Zilles, K. Multiple movement representations in the human brain: An event-related fMRI study. J. Cogn Neurosci. 2002b, 14: 769–784.
Vitacco, D., Brandeis, D., Pascual-Marqui, R. and Martin, E. Correspondence of event-related potential tomography and functional magnetic resonance imaging during language processing. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17: 4–12.
Wise, S.P., Boussaoud, D., Johnson, P.B. and Caminiti, R. Premotor and parietal cortex: Corticocortical connectivity and combinatorial computations. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1997, 20: 25–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Praeg, E., Esslen, M., Lutz, K. et al. Neuronal Modifications During Visuomotor Association Learning Assessed by Electric Brain Tomography. Brain Topogr 19, 61–75 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-006-0013-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-006-0013-y