Abstract.
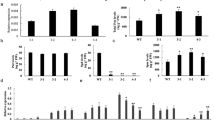
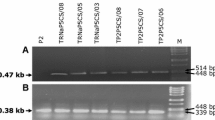
We investigated how over-expression of a cDNA for human ornithine decarboxylase (odc) affects the polyamine pools in transgenic rice. We further investigated tissue-specific expression patterns and product accumulation levels of the transgene driven by either constitutive or seed-specific promoters. Our results indicate that: (1) whereas the expression of a heterologous arginine decarboxylase (adc) cDNA in rice resulted in increased putrescine and spermine levels only in seeds, plants engineered to express odc cDNA exhibited significant changes in the levels of all three major polyamines in seeds and also in vegetative tissues (leaves and roots); (2) there was no linear correlation between odc mRNA levels, ODC enzyme activity and polyamine accumulation, suggesting that control of the polyamine pathway in plants is more complex than in mammalian systems; (3) ODC activity and polyamine changes varied in different tissues, indicating that the pathway is regulated in a tissue-specific manner. Our results suggest that ODC rather than ADC is responsible for the regulation of putrescine synthesis in plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lepri, .O., Bassie, .L., Safwat, .G. et al. Over-expression of a cDNA for human ornithine decarboxylase in transgenic rice plants alters the polyamine pool in a tissue-specific manner. Mol Gen Genomics 266, 303–312 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380100557
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380100557